

An element becomes unstable when the number of neutrons in it is abnormally high. Neutrons produce gamma rays during radioactivity. They are mainly responsible for radioactive properties of an element.
Properties of subatomic particles free#

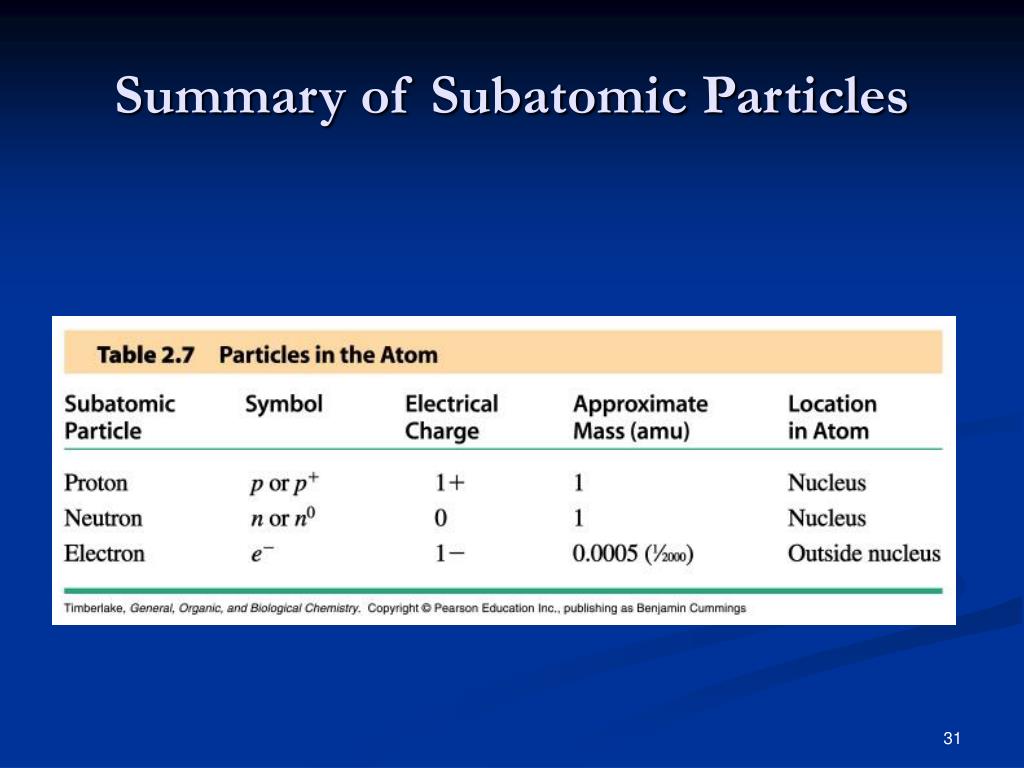
Protons are also defined as a Hydrogen ion H+, since a hydrogen ion contains only a positively charged proton.Protons are divisible subatomic particles unlike electrons, and they are composed of up to three fundamental particles, which are known as quarks.Thus, they are nuclear particles, nucleons. Protons reside in the nucleus of an atom along with neutrons.Protons are subatomic particles having an electric charge of positive +1 elementary charge.Properties of subatomic particles protons The radius of an electron according to classical physics is `2.8179*10^-15` m, whereas in actual quantum physics experiments, it has been found to be around `10^-22` meters.The mass of an electron is `9.109*10^-31` kilogram. Since electrons are the lightest subatomic particles, they make up for only about 0.6% of an atom’s total mass.The term ‘electron’ was coined by George Stoney in 1894, and electrons were discovered as a particle in 1897 by J.J.Electrons are the sole reasons for the different chemical properties of atoms, since all chemical reactions involve the exchange of electrons only.Electrons have properties of a wave as well as those of a particle, and thus they show a dual nature like light.It is also represented using the symbol -e. This elementary charge is regarded as a physical constant. An electron is an elementary particle, that is, it is an indivisible subatomic particle, as it possesses no sub-components.This is because the number of electrons determines chemical properties, and all three isotopes have one electron in their atoms.Properties of subatomic particles electrons For example, carbon-12 is an isotope of carbon with a mass number of 12.Īll three isotopes of hydrogen have identical chemical properties.
IsotopeĪn isotope is named after the element and the mass number of its atoms. Hydrogen-1 is the most abundant (most common) isotope of hydrogen. Isotopes of an element have:Īll hydrogen atoms contain one proton (and one electron ), but they can contain different numbers of neutrons. Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. Atoms of the same element must have the same number of protons, but they can have different numbers of neutrons.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
